Blockchain Development Costs & Features – A Complete Guide

Blockchain development costs and features are crucial considerations for businesses venturing into this latest development technology. The cost of blockchain app development services varies significantly, influenced by factors like complexity, platform choice, and blockchain development team expertise. Initial expenses typically involve hiring skilled blockchain developers and setting up infrastructure.
Blockchain app development services offers features like decentralization, immutability, and security, making it suitable for various blockchain application development services, from cryptocurrency development to blockchain supply chain management. Smart contracts blockchain development enable automation and reduce intermediaries, streamlining processes.
Ongoing maintenance costs, including updates and security measures, should not be overlooked. Scalability can also affect expenses as blockchain development networks grow.
Blockchain development costs encompass initial investments, ongoing maintenance, and scalability considerations. Its features, such as Decentralized Exchange Software Development Services and smart contracts blockchain app development services, can revolutionize industries but require careful planning and budgeting.
A Complete Guide to Blockchain Development According Comfygen
According to Comfygen as a leading blockchain app development agency, they present an article; a complete guide on Blockchain is given in the Blockchain Development. This is a complete guide to an introduction to blockchain, along with types of blockchain development services, key features, factors, and blockchain app development costs.
Blockchain Market Growth Industry
The global blockchain development technology market is undergoing a remarkable and exponential growth trajectory, underpinned by staggering statistics. In 2022, the market boasted a valuation of USD 11.14 billion, and it is poised to skyrocket further, with projections indicating a surge to USD 17.57 billion in 2023. However, the most astounding revelation lies in the forecasted growth over the next decade, where the blockchain development market is anticipated to reach a staggering USD 469.49 billion by 2030. This phenomenal ascent is marked by a remarkable Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 59.9%. Such meteoric expansion underscores the transformative power of blockchain development technology across various sectors and industries. Its capacity to enhance security, transparency, and efficiency in processes ranging from finance and supply chain management to healthcare and government services is driving this unprecedented growth. As blockchain app development agency continues to disrupt traditional paradigms and forge new avenues of innovation, it cements its position as a linchpin in the future of technology and global economic development. The blockchain development market’s evolution promises not just substantial financial gains but also a seismic shift in how industries operate and collaborate on a global scale.
Thanks for fortune business insights
Introduction Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Agency has emerged as a transformative blockchain development technology that is reshaping the way businesses and industries operate. This revolutionary technology, initially created as the foundation for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has transcended its initial purpose and found applications across a wide range of sectors. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the world of blockchain development, understanding its essence and unraveling its profound significance across various industries.
What is Blockchain Development?
Blockchain development is the process of creating and maintaining blockchain-based systems and blockchain applications development services. At its core, a blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. These transactions are grouped into blocks and securely linked through cryptographic hashes, forming an immutable chain. Blockchain developers use coding languages like Solidity Blockchain development for Ethereum Blockchain development or C++ for Bitcoin Blockchain development to design and implement smart contracts Blockchain development, decentralized applications (DApps)Blockchain development, and consensus mechanisms. Blockchain Development Company emphasizes key principles such as transparency, security, immutability, and decentralization. It has far-reaching applications across various industries, including finance, supply chain, healthcare, and more, revolutionizing how data is stored, verified, and transacted in a trustless and efficient manner. As blockchain development technology continues to evolve, blockchain developers play a pivotal role in harnessing its potential for innovative solutions and transformative changes in the digital landscape.
Importance of Blockchain in Various Industries
Blockchain development technology has gained immense importance across various industries due to its transformative capabilities. One of its primary contributions is to enhance security and transparency. In the financial sector, blockchain development services has revolutionized the way transactions are conducted, providing secure and efficient alternatives to traditional decentralized banking app systems. It reduces fraud, improves cross-border payments, and enables financial inclusion for underserved populations.
In supply chain management, blockchain development ensures transparency and traceability of goods from origin to destination. This is vital in reducing fraud, and counterfeiting, and ensuring the authenticity of products, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals and food app development.
Healthcare blockchain app development is another sector where blockchain development is making a significant impact. Patient data can be securely stored and shared among healthcare blockchain development service providers, ensuring data integrity and privacy. This streamlines processes, reduces, errors, and ultimately enhances patient care.
The real estate blockchain app development industry benefits from blockchain’s efficiency in property transactions and title management. It simplifies complex processes, reduces fraud, and increases transparency.
In the energy sector, blockchain enables peer-to-peer marketplace for cryptocurrency energy trading, making renewable energy sources more accessible and affordable.
Overall, In blockchain development company is an importance lies in its ability to provide trust, security, and efficiency in various industries, leading to cost savings, reduced fraud, and improved services. Its potential continues to grow as businesses and organizations explore innovative ways to leverage this technology.
Get Free Demo For Blockchain Development
Types of Blockchain Development
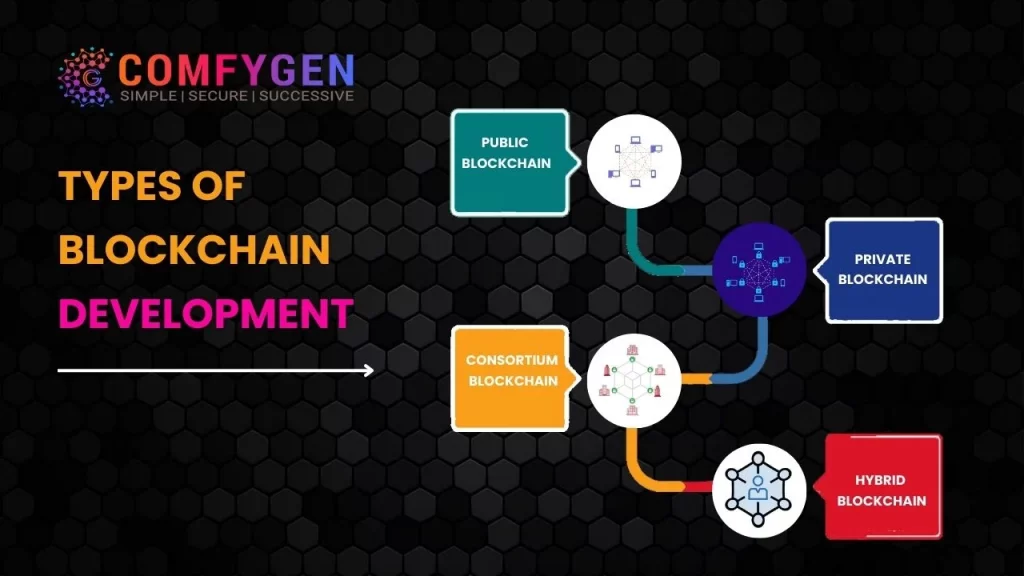
Blockchain technology has diversified to accommodate various use cases and organizational needs. To grasp the breadth of blockchain development, we must explore its distinct types:
- Public Blockchain Development
- Private Blockchain Development
- Consortium Blockchain Development
Each type offers unique features and use cases, making them suitable for different scenarios.
Public Blockchain Development:
A Public Blockchain Development is a decentralized and permissionless digital ledger that is open to anyone and everyone. It operates on a global network of computers, or nodes, where transactions are recorded in a transparent and immutable manner. Key characteristics of public blockchains include decentralization, open access, security, and transparency.
Decentralization means that there is no central authority or intermediary governing the network. Instead, it relies on a consensus mechanism, such as proof of work (PoW blockchain development) or proof of stake (PoS), to validate and secure transactions. Open access means that anyone can participate in the network, create wallets, and transact without needing approval, making it highly inclusive.
Security is ensured through advanced cryptographic techniques and the consensus process, making public blockchains highly resistant to tampering and fraud. Transparency is a fundamental feature, as all transactions are visible to anyone on the network, promoting trust and accountability.
Public Blockchain Development are most famously associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin Blockchain Development and Ethereum Blockchain Development, where users can send and receive digital assets without relying on traditional financial intermediaries like banks. Additionally, they serve as platforms for decentralized applications (DApps Blockchain Development) and smart contracts Blockchain Development, enabling a wide range of innovative use cases beyond digital currencies.
Private Blockchain Development:
The Private Blockchain Development is a permissioned and centralized digital ledger designed for a select group of participants, typically organizations or individuals with a vested interest. Unlike Public Blockchain Development, Private Blockchain Development restrict access, requiring permission to join the network. Key characteristics of private blockchain development include permissioned access, centralized governance, data privacy, and improved performance.
Permissioned access means that participants must be approved to join the network, ensuring that only trusted entities can validate transactions and maintain the blockchain. Governance is often centralized, with a single entity or consortium of organizations overseeing the network’s rules and operations, allowing for faster decision-making and updates.
Data privacy is a priority in private blockchain development, and they often employ encryption and restricted visibility to protect sensitive information. Moreover, private blockchains tend to have higher transaction throughput and faster consensus mechanisms compared to public blockchains, making them suitable for use cases where efficiency and control are paramount.
Private blockchain development find applications in supply chain management, finance, healthcare, and other sectors that require secure, controlled, and efficient data management without the openness of public blockchains.
Consortium Blockchain Development:
A consortium blockchain development is a semi-decentralized digital ledger that combines elements of both public and private blockchains. It operates within a network where multiple trusted entities or organizations collaborate. Key characteristics of consortium blockchain development include limited access, shared control, trust among members, and efficiency.
Limited access means that consortium blockchain development are accessible only to a select group of participants who are known and trusted by the consortium members. These participants usually require permission to join the network, ensuring that it remains semi-private.
Shared control is a crucial feature, as governance decisions are often made collectively by the participating entities. This democratic approach enables consensus among consortium members and helps maintain the integrity of the network.
Trust plays a central role in consortium blockchain development, as participants rely on the trust they have in each other, often through legal agreements or contracts, to ensure the security and reliability of the Blockchain Development Company.
Efficiency is another advantage of consortium blockchain development, as they strike a balance between the control of private blockchain development and the trust of public blockchain development ones. They are well-suited for use cases where multiple organizations need to collaborate securely and streamline processes while maintaining a level of trust and efficiency.
Key Features of Blockchain Development
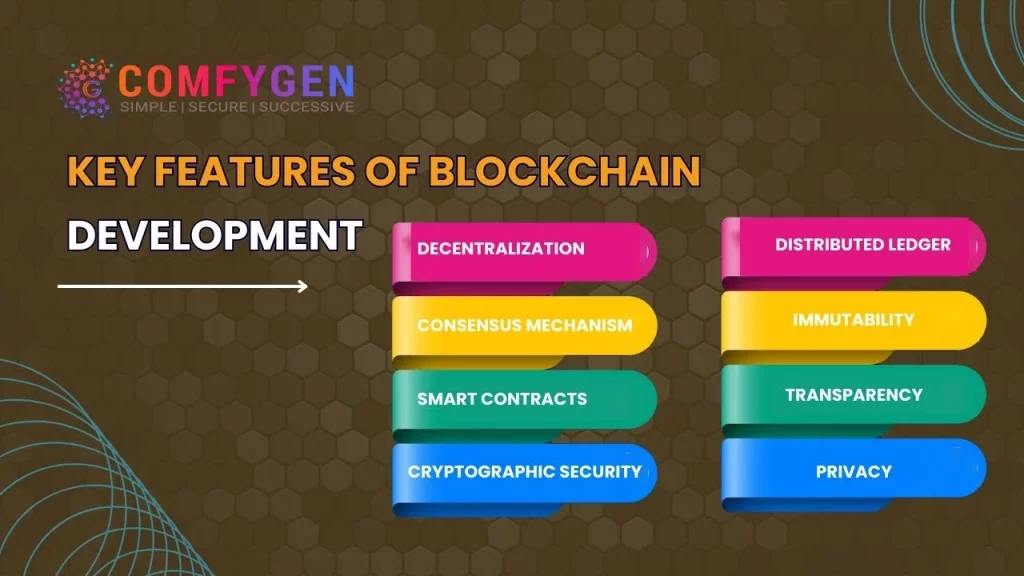
Blockchain development encompasses a range of critical features that underpin its transformative potential across various industries. These features include decentralization:
- Immutable ledger
- Smart contracts
- Transparency and auditability
- Enhanced security and data privacy
- Understanding these features is essential to grasp the profound impact of blockchain app development technology.
Decentralization:
Decentralization is one of the key features of blockchain development, contributing to its transformative potential. It involves the distribution of control and authority across a network of computers (nodes) rather than relying on a central entity. Here are some essential aspects of decentralization in the blockchain development:
- Resilience: Decentralization enhances network resilience as there is no single point of failure. If one node or part of the network goes offline, the system continues to operate, ensuring uninterrupted service.
- Security: Distributed control and cryptographic techniques make it challenging for malicious actors to compromise the network. This robust security is especially crucial in financial transactions and sensitive data storage.
- Trust: Decentralization eliminates the need for intermediaries, promoting trust among participants. Transactions are verified collectively, reducing the risk of fraud and disputes.
- Autonomy: Participants have greater autonomy and control over their assets and data in a decentralized system. They can transact directly without relying on centralized authorities.
- Transparency: Decentralization doesn’t sacrifice transparency; in fact, it enhances it. All transactions are recorded on a public blockchain development ledger visible to all participants, promoting accountability and trust.
- Inclusivity: Decentralization opens up opportunities for individuals and organizations worldwide to participate in the network without the need for special permissions, fostering inclusivity and innovation.
In essence, decentralization empowers individuals and organizations by providing a secure, transparent, and resilient framework for conducting transactions and managing data, making it a cornerstone of blockchain development
Immutable Ledger:
The immutability of a blockchain ledger is a key feature that sets it apart from traditional databases. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes permanent and tamper-proof. This immutability is achieved through cryptographic hashing, where each block contains a unique reference to the previous block, creating a chain of blocks that is nearly impossible to alter.
The immutable ledger feature has profound implications for data integrity and trust. It ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, preventing fraud and ensuring the integrity of historical records. In industries like healthcare blockchain development and law, where accurate and unchangeable records are crucial, blockchain’s immutable ledger provides a reliable blockchain development solution.
Smart Contracts:
Smart contracts blockchain development are self-executing, programmable contracts that automatically enforce the terms and conditions of an agreement when predefined conditions are met. These contracts are encoded in code and run on the blockchain development, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of disputes or breaches of contract.
Smart contracts blockchain development have wide-ranging applications, including in finance, supply chain management, and decentralized applications (DApps blockchain development). For instance, in financial services, smart contracts automate processes like loan approvals, reducing paperwork and human errors. In the supply chain, they can automatically trigger payments and update inventory levels when goods are delivered, streamlining operations and improving efficiency.
Transparency and Auditability:
Transparency and auditability are fundamental features of blockchain development, essential for building trust and accountability in digital ecosystems.
Transparency in blockchain development refers to the openness of the ledger, where all transactions are recorded in a public blockchain development and accessible manner. This transparency ensures that all participants in the network have access to the same information, creating a level playing field and reducing the potential for fraud or manipulation. It promotes trust among users as they can independently verify transactions.
Auditability goes hand in hand with transparency, as it enables a complete and tamper-proof historical record of all transactions. Once data is recorded on the blockchain app development, it becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or deleted. This feature ensures the integrity of historical records and simplifies auditing processes, making it easier to track and verify the authenticity of transactions.
Together, transparency and audibility in blockchain development Industry have wide-ranging applications across industries, from financial services and supply chain management to healthcare blockchain development and voting systems. They provide a reliable and transparent foundation for secure and accountable transactions and data management.
Enhanced Security:
Blockchain employs advanced cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and data. Transactions are cryptographically signed, and consensus mechanisms like proof of work (PoW blockchain development) or proof of stake (PoS blockchain development) ensure that malicious actors cannot easily manipulate the network. Additionally, the decentralized nature of blockchain means that there is no central point of attack.
Enhanced security is vital in industries where data integrity and privacy are paramount. In finance, blockchain development provides a secure blockchain development platform for transactions, reducing the risk of hacks and fraud. In healthcare blockchain development, patient data can be stored securely on the blockchain, protecting it from unauthorized access and breaches.
Data Privacy:
Data privacy is a critical concern in the digital age, and blockchain development offers solutions to address these concerns. While blockchain development provides transparency, it also allows for data privacy through encryption and controlled access mechanisms. Participants can control who has access to their data, and sensitive information can be encrypted, ensuring that it remains confidential.
In industries like healthcare blockchain development, where patient data is highly sensitive, blockchain development allows patients to maintain control over their medical records while securely sharing them with authorized healthcare providers. Similarly, in supply chain management, confidential business data can be protected while still benefiting from the transparency and traceability offered by the blockchain development.
Factors Affecting Blockchain Development Cost
Blockchain development costs can vary significantly depending on several factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses and organizations seeking to embark on blockchain projects. Here, we will explore the key elements that influence blockchain development costs:
Complexity of the Project:
The complexity of a blockchain app development project is a primary driver of development costs. Projects can range from relatively straightforward implementations to highly complex, multi-faceted systems. Key factors contributing to complexity include:
- Use Case Complexity: Some use cases, such as simple cryptocurrency blockchain development transactions, are less complex than those involving smart contracts blockchain development, complex consensus mechanisms, or intricate business logic.
- Scalability Requirements: Developing a blockchain app development services that can handle a high volume of transactions and scale as needed can be more complex and costly.
- Integration with Existing Systems: If the blockchain development services needs to integrate with legacy systems or external data sources, the complexity increases, impacting development costs.
Highly complex projects often require more extensive development, testing, and ongoing maintenance, which can drive up expenses significantly.
Development Team Experience:
The experience and expertise of the blockchain development team play a crucial role in determining blockchain development services costs. Highly skilled and experienced blockchain developers typically command higher rates. Factors to consider include:
- Blockchain development Specialization: Blockchain Developers with a deep understanding of blockchain development technology, including its underlying principles and various blockchain development platforms (e.g., Ethereum blockchain development, Hyperledger blockchain development), are in high demand and often come at a premium.
- Smart Contract Development: Building smart contracts blockchain development, which are self-executing codes on the blockchain development, requires specialized skills. Blockchain Developers proficient in Solidity blockchain development (for Ethereum blockchain development) or other blockchain development-specific languages tend to charge more.
- Security Expertise: Security is paramount in blockchain development. Teams with expertise in securing blockchain development networks and smart contracts blockchain development are crucial for safeguarding against vulnerabilities and attacks.
Choosing a blockchain development team with the right skills and experience is essential for the success and security of a blockchain development project, but it can impact project costs.
Technology Stack:
The technology stack chosen for blockchain development can have a significant impact on costs. Factors to consider include:
- Blockchain Platform: Different blockchain development platforms have varying levels of complexity and costs associated with development. For instance, public blockchains like Ethereum blockchain development may have higher gas fees than private blockchains like Hyperledger Fabric blockchain development.
- Consensus Mechanism: The choice of consensus mechanism (e.g., proof of work blockchain development, proof of stake blockchain development) can influence the development effort and costs. For example, implementing a unique consensus mechanism requires additional blockchain development work.
- Database and Storage: The selection of database systems, storage solutions, and cloud blockchain development providers can impact costs. Scalable and high-performance options may come at a premium.
- Development Tools: Using specialized blockchain development frameworks process and tools can streamline development but may incur licensing or subscription fees.
Making informed decisions about the technology stack is essential to balancing project requirements and budget constraints.
Requirements and Customizations:
The specific requirements and customizations needed for a blockchain app development project can significantly affect costs. These include:
- Functional Requirements: Complex features or functionalities, such as multi-signature wallets, governance mechanisms, or complex smart contracts, can increase development costs.
- User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX): Developing Ui/Ux Development an intuitive and user-friendly interface often requires additional design and development work, impacting costs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and blockchain development industry standards may necessitate additional development and auditing, increasing project expenses.
- Privacy and Security Features: Implementing advanced privacy and security measures, such as zero-knowledge proofs or encryption, can add complexity and costs.
- Integration: If the blockchain development project needs to integrate with other systems or APIs, additional development work is required, influencing costs.
Customizations tailored to the project’s specific needs are essential but can add complexity and expenses to the development process.
Deployment and Maintenance:
Deployment and ongoing maintenance are often underestimated factors that impact blockchain development costs:
- Deployment: Launching the blockchain network, setting up nodes, and configuring the infrastructure require careful planning and resources. Costs may include hosting, network setup, and deployment tools.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Rigorous testing, including security audits, load testing, and functional testing, is crucial to ensuring the blockchain’s reliability and security. These activities come with their own associated costs.
- Ongoing Maintenance: After deployment, ongoing maintenance, monitoring, and updates are essential to keep the blockchain secure and operational. Maintenance costs can include patching vulnerabilities, addressing bugs, and upgrading the network.
- Scalability Planning: As the network grows, scalability solutions may be needed, which can involve additional development and costs.
- Community Support: Some blockchain projects require community support and engagement, which entails community management costs.
Estimating Blockchain Development Cost
Estimating blockchain development costs involves considering factors like project complexity, development team rates (hourly or fixed price), and a breakdown of expenses across phases (planning, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance). Additional costs include consultation, legal compliance, training, and third-party services. Contingency budgeting and thorough analysis are essential to accommodating unforeseen challenges. Accurate budgeting ensures sufficient resources for successful blockchain project execution.
Hourly Rate vs. Fixed Price:
When estimating blockchain development company costs, one of the fundamental decisions to make is whether to opt for an hourly rate or a fixed-price contract. Each approach has its advantages and considerations:
- Hourly Rate: Under an hourly rate model, you pay the development team based on the number of hours worked. This approach offers flexibility, allowing you to adjust the project scope and requirements as you go. However, it can lead to uncertainty in terms of final costs if the project evolves or encounters unforeseen challenges. It is important to establish clear communication and regular reporting to monitor progress and costs.
- Fixed Price: In a fixed-price contract, you agree on a predetermined total cost for the entire project. This approach provides budget certainty, as you know the exact cost upfront. However, it requires a comprehensive project scope definition, and any changes or additions to the scope can lead to additional charges. Additionally, it may be less flexible if project requirements evolve during development.
BlockChain Technology Application developed by major Mobile App Development occupation, with a 3000+ experienced team size, range in cost – range from $450,000 to $1,500,000
The cost of developing an Blockchain app by a mid-cap company with a team of 1,000+ experts, such as Comfygen, ranges from $40,000 to $300,000.
Blockchain Application cost between $2,000 and $25,000 when created by independent contractors or small shops with teams of 10 to 50 experts.
The choice between these models often depends on project complexity, budget constraints, and your level of confidence in the project scope. For well-defined and straightforward projects, a fixed-price contract may be suitable. For projects with evolving requirements or high complexity, an hourly rate model can provide more flexibility.
Cost Breakdown by Blockchain Development Phases:
Breaking down the blockchain development process into phases can help estimate costs more accurately. Here is a typical cost breakdown:
- Project Planning: This phase involves project scoping, requirement gathering, and planning. Costs may include project management and consultation fees to determine the project’s feasibility and requirements.
- Design and Prototyping: Designing the user interface (UI), creating smart contracts, and creating prototypes may involve costs related to design, user experience (UX), and front-end development.
- Development: The core development phase includes coding the blockchain development, smart contracts, and any necessary Diamond Exchange APIs or integrations. Costs are primarily associated with development labor.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Rigorous testing, including security audits, load testing, and functional testing, is essential for blockchain projects. Costs cover testing tools, infrastructure, and QA specialists.
- Deployment: Launching the blockchain network, setting up nodes, and configuring infrastructure may incur costs for hosting, network setup, and deployment tools.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Post-launch, ongoing maintenance, monitoring, and updates are vital for network security and stability. Costs encompass patching vulnerabilities, addressing bugs, and network upgrades.
- Community and User Support: If the project requires community support or user assistance, community management and customer support costs are applicable.
It’s essential to allocate your budget based on the project’s specific needs and priorities. Some phases may require more resources and investment than others, depending on project complexity and goals.
Additional Costs to Consider:
Estimating blockchain development costs goes beyond the core development and includes additional factors that can impact the budget:
- Consultation and Strategy: Engaging blockchain consultants to strategize and plan the project can incur additional costs. Their expertise can be invaluable for making informed decisions.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations may involve legal consultation and compliance-related costs.
- Training and Education: If your team requires blockchain training or education to work on the project effectively, consider the cost of training programs or workshops.
- Third-Party Services: Depending on the project’s requirements, you may need to integrate with third-party services or oracles, which may involve licensing or subscription fees.
- Customization and Integration: Tailoring the blockchain solution to your specific needs and integrating it with existing systems may require additional development and customization costs.
- Data Storage and Bandwidth: Blockchain networks often involve data storage and bandwidth costs, particularly for public blockchains. Ensure you estimate these costs, if applicable.
- Marketing and Adoption: Promoting the blockchain project and gaining user adoption may require marketing efforts and associated costs.
- Scalability Planning: As the network grows, scalability solutions may be needed, which can involve additional development and costs.
- Contingency Budget: It’s wise to allocate a portion of your budget for unexpected issues, delays, or scope changes that may arise during development.
- Currency Exchange Rates: For international projects or if working with cryptocurrencies, fluctuations in exchange rates can impact costs.
- Post-Deployment Audits: Conducting security audits and code reviews after deployment may be necessary to identify vulnerabilities or issues, incurring additional expenses.
- Insurance: Some projects may require cybersecurity insurance to mitigate risks associated with security breaches or unforeseen events.
Get a Free Quote Today!
What is the Blockchain Development Process?
The blockchain development process involves several key phases to create decentralized applications (DApps) and blockchain networks. It begins with conceptualization, where the project’s goals and use cases are defined. Next, requirements are gathered, specifying the DApp’s features and technical specifications. Afterward, the design phase involves creating the architecture and user interface. Development follows, where smart contracts and the blockchain’s core code are written and tested. Once the code is ready, deployment occurs, launching the blockchain or DApp on a chosen network. Post-deployment, ongoing maintenance, and updates are essential to ensuring the system’s reliability and security. Throughout this process, collaboration among developers, stakeholders, and often the blockchain community is crucial for success, as blockchain development is a dynamic and evolving field that requires continuous innovation and adaptation to meet the needs of various industries.
This is a complete guide on the blockchain development process, tools, case studies of blockchain development, blockchain application services, the tech stack for blockchain application development, and much more about blockchain. This blog describes a complete guide to blockchain development.
What are the Best Blockchain App Development Tools?
Blockchain technology has revolutionized various industries, and the development of decentralized applications (DApps) has become increasingly popular. To excel in this field, developers rely on a set of essential tools that streamline the process. Here are some of the best blockchain development tools that have made their mark:
- Geth: Geth, short for Go Ethereum, stands as a premier blockchain app development tool. It functions as a command-line interface, enabling seamless interaction with the Ethereum blockchain. Its capabilities include account management, mining, and smart contract handling, making it an indispensable choice for Ethereum developers.
- Remix: Remix is a web-based IDE (Integrated Development Environment) designed for Ethereum smart contract development. It offers a user-friendly interface and features like real-time code compilation and debugging.
- Mist: Mist is another Ethereum-specific tool, that serves as a DApp browser and wallet. It enables users to explore and interact with decentralized applications seamlessly.
- GanacheCLI: GanacheCLI is an indispensable blockchain app development tool, serving as a local Ethereum blockchain emulator. It facilitates efficient testing and development by providing a customizable and isolated blockchain environment. Developers rely on GanacheCLI to ensure the reliability and functionality of their Ethereum-based decentralized applications before deploying them to the mainnet.
- Solium EtherScripter: Solium EtherScripter is a code linter designed specifically for Solidity, Ethereum’s smart contract programming language. It helps developers write clean and error-free code.
- Embark: Embark is a leading-edge blockchain app development tool, offering a comprehensive framework for Ethereum DApp creation and deployment. It simplifies the development process by providing a suite of tools and features, streamlining smart contract creation, testing, and deployment. Embark empowers developers to build secure and efficient decentralized applications.
- Metamask: Metamask, a pivotal blockchain app development tool, serves as an Ethereum wallet and browser extension. It offers secure account management and seamless interaction with DApps. Developers rely on Metamask for easy integration of Ethereum features into their applications.
- Blockchain Testnet: Blockchain Testnet is a crucial tool for blockchain app development. It provides a risk-free environment to test smart contracts and DApps before deployment on the mainnet. Hire Blockchain App Developers depend on Testnets for identifying and resolving issues and ensuring the reliability of their applications.
- Truffle: Truffle stands as a premier blockchain app development tool. It offers a comprehensive development framework for Ethereum, encompassing smart contract compilation, testing, and deployment. Trusted by developers, Truffle streamlines the process of building secure and efficient decentralized applications.
These blockchain development tools play a pivotal role in simplifying and enhancing the development process for DApps and smart contracts.
Case Studies :
Blockchain technology has garnered immense attention across various industries due to its potential to revolutionize traditional processes, enhance security, and improve transparency. However, implementing blockchain solutions involves significant development costs, which can vary depending on the specific industry and project requirements. In this article, we will explore three case studies to analyze the blockchain development costs associated with supply chain management, financial applications, and healthcare solutions.
Blockchain Development Cost for a Supply Chain Solution
Supply chain management is a complex and multi-faceted industry that often faces issues related to inefficiency, fraud, and a lack of transparency. Blockchain technology has the potential to address these challenges by providing a decentralized and immutable ledger for tracking goods and transactions. Let’s delve into the factors influencing the development cost of a blockchain supply chain solution:
- Scope and Complexity of the Project: The first determinant of cost is the scope and complexity of the supply chain solution. A simple blockchain system for tracking product shipments may cost less than a comprehensive solution that integrates with various stakeholders, including manufacturers, suppliers, distributors, and retailers. Complex projects involve more development effort and, therefore, higher costs.
- Technology Stack: Technology Stack the choice of blockchain platform and associated technologies can significantly impact blockchain development costs. Popular options like Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, and Corda offer different features and scalability. Depending on the specific project requirements, licensing fees, and development resources, the cost of the technology stack can vary.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Many supply chain businesses already have legacy systems in place. Integrating a blockchain solution with these systems can be a challenging and costly process. The need for middleware, data migration, and API development adds to the overall development cost.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing agreements that automate processes on the blockchain. Developing complex smart contracts for supply chain functions, such as automated payments or quality assurance, requires additional development resources, thereby increasing costs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards, such as GDPR or FDA requirements in healthcare, adds complexity to the development process. Ensuring that the blockchain solution adheres to these regulations necessitates legal consultations and compliance measures, which can be expensive.
- Security Measures: Supply chain solutions must prioritize security to protect sensitive data and prevent fraud. Implementing robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and auditing, adds to the development cost.
- Maintenance and Updates: Maintenance and updates of a blockchain supply chain solution involve ongoing efforts to ensure system functionality, security, and compliance. This includes fixing bugs, implementing security patches, adapting to changing business needs, and addressing regulatory changes. These activities are essential to keeping the solution running efficiently and securely over time.
Blockchain Development Cost for a Financial Application
Blockchain technology has disrupted the financial industry by providing faster and more secure transaction processing, reducing fraud, and enabling innovative financial products. Here, we analyze the factors influencing the development cost of a blockchain-based financial application:
- Regulatory Compliance: The financial sector is heavily regulated, and blockchain applications must adhere to strict regulatory standards. Legal consultations, compliance assessments, and ongoing monitoring are essential components that contribute to development costs.
- Core Functionality: The complexity of the financial application’s core functionality significantly impacts development costs. Building a simple blockchain-based payment system may be less expensive than creating a decentralized exchange or a complex lending platform.
- Security: Security in a financial blockchain application entails substantial costs, including implementing robust measures like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and anti-fraud mechanisms. Additionally, expenses associated with compliance, regular security audits, and ongoing monitoring are essential to safeguarding sensitive financial data and protecting against potential threats and vulnerabilities.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts in financial blockchain development require investments in their development, auditing, and integration with the application’s infrastructure. These self-executing contracts automate financial processes, but costs include skilled developers, audit expenses, and ongoing maintenance to ensure they function correctly, securely, and efficiently.
- Scalability: Financial applications must handle high volumes of transactions. Ensuring scalability to accommodate growing user bases requires additional development work and potentially higher costs.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Many financial institutions have legacy systems in place. Integrating blockchain applications with these systems may involve significant development effort, middleware development, and data migration, contributing to the overall cost.
- Tokenization: Tokenization is a financial blockchain application that involves creating digital representations of real-world assets like securities or real estate. The associated costs include developing tokenization protocols, ensuring regulatory compliance, issuing tokens, and maintaining the infrastructure for asset-backed tokens. These expenses are essential for enabling asset trading and ownership on the blockchain.
- Testing and Auditing: Rigorous testing and security audits are critical in financial applications to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance. The cost of third-party audits and penetration testing should be considered.
Blockchain Development Cost for a Healthcare Solution

Blockchain technology holds tremendous promise in the healthcare industry, improving data interoperability, patient records management, and drug supply chain tracking. Let’s explore the factors affecting the development cost of a blockchain healthcare solution:
- Data Security and Privacy: Healthcare solutions must prioritize data security and patient privacy. Implementing robust encryption, access controls, and compliance with healthcare regulations (e.g., HIPAA) are essential but costly components.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) Integration: Integrating blockchain with existing EHR systems can be complex and require custom development work. Data migration, API development, and ensuring data consistency across systems contribute to costs.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts can automate various healthcare processes, such as insurance claims processing and consent management. Developing and auditing these contracts for accuracy and compliance can incur additional expenses.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with healthcare regulations, including data protection laws and clinical standards, is a paramount concern. Legal consultations, compliance assessments, and ongoing monitoring contribute to development costs.
- Interoperability: Achieving interoperability necessitates investment in standardized protocols and interfaces for seamless data exchange between various healthcare systems and institutions. Development efforts and resources are directed towards ensuring compatibility and efficient sharing of patient information, ultimately improving healthcare data management.
- Supply Chain Tracking: Blockchain can help track the pharmaceutical supply chain to combat counterfeit drugs. Developing a comprehensive tracking system that involves multiple stakeholders, such as manufacturers, distributors, and pharmacies, can be complex and costly.
- Electronic Prescriptions: Implementing electronic prescriptions in a healthcare blockchain solution involves development costs for secure interfaces between healthcare providers and pharmacies. Ensuring data accuracy, compliance with regulations, and robust security measures add to expenses, ensuring a reliable and efficient prescription process on the blockchain.
- Maintenance and Updates: Like any other industry, healthcare blockchain solutions require ongoing maintenance, updates, and support. These recurring costs should be factored into the project budget.
Best Practices for Managing Blockchain Development Costs
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize industries by enhancing security, transparency, and efficiency. However, developing blockchain solutions can be costly and complex. To ensure the successful implementation of blockchain projects without exceeding budgetary constraints, it’s essential to follow best practices for managing development costs. In this article, we will explore four key practices to help organizations effectively control and optimize their blockchain development expenses.
Define Clear Objectives and Requirements
Before embarking on a blockchain development project, it is imperative to define clear objectives and requirements. This foundational step sets the stage for cost management throughout the project’s lifecycle.
Key Considerations:
- Business Objectives: Clearly define the specific goals the blockchain solution aims to achieve. For instance, in supply chain management, the objective might be to improve transparency and reduce fraud.
- Functional Requirements: Document the functional requirements of the blockchain system. What features and capabilities are necessary to meet the objectives? Prioritize these requirements based on their importance.
- Technical Specifications: Specify the technical details, such as the choice of blockchain platform, consensus mechanism, and scalability requirements. Ensure alignment with the project’s goals.
Benefits:
- Cost Avoidance: By defining objectives and requirements upfront, you can avoid costly scope changes and project pivots that can derail timelines and budgets.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate resources more efficiently by focusing on elements that directly contribute to achieving the project’s objectives.
- Risk Mitigation: A clear understanding of requirements helps identify potential risks and challenges early, enabling proactive mitigation.
Prioritize Features and Functionality
Not all features are created equal, and prioritizing them is crucial for managing development costs effectively. A well-defined feature prioritization strategy ensures that the most critical elements are addressed within budget constraints.
Key Considerations:
- Critical Features: Identify and prioritize features that are essential to achieving the project’s objectives. These features should be developed first to create a functional minimum viable product (MVP).
- Nice-to-Have Features: Distinguish between essential features and those that are nice to have but not critical. These can be included in later development phases if the budget allows.
- User Feedback: Collect feedback from stakeholders and end-users to refine feature priorities. This iterative approach helps ensure that resources are allocated to high-impact functionalities.
Benefits:
- Cost Control: By focusing on critical features, you can develop a functional blockchain solution within budget constraints.
- Time-to-Market: Prioritization accelerates the development process, enabling quicker deployment of essential functionality.
- Adaptability: As the project progresses, the flexibility to adjust feature priorities based on feedback and changing requirements ensures that the solution remains aligned with business needs.
Optimize the Development Process and Resources
Efficient resource allocation and streamlined development processes are essential for controlling costs while delivering a quality blockchain solution.
Key Considerations:
- Skilled Team: Assemble a team with expertise in blockchain development, smart contract programming, and relevant technologies. Skilled professionals can deliver high-quality code more efficiently.
- Iterative Development: Adopt an iterative development approach, such as Agile or Scrum, to continually improve the solution while managing costs. Frequent iterations allow for course corrections and feature adjustments.
- Use of Open Source: Leverage open-source blockchain platforms and libraries to reduce development costs. Building on existing frameworks can significantly accelerate development.
- Outsourcing: Consider outsourcing specific development tasks to external experts or development firms. This can be cost-effective, especially for specialized blockchain components.
Benefits:
- Cost Efficiency: Optimizing development resources and processes minimizes inefficiencies and reduces development time and costs.
- Quality Assurance: A skilled team and iterative development contribute to a higher-quality solution, reducing the need for costly post-launch fixes.
- Flexibility: A well-structured development process allows for adaptability to changing project requirements without significant cost overruns.
Regularly Review and Evaluate Costs
Cost management should be an ongoing practice throughout the blockchain development project. Regularly reviewing and evaluating costs helps maintain financial discipline and ensures that the project remains on track.
Key Considerations:
- Budget Monitoring: Continuously monitor the project budget to track spending against the allocated resources. Identify any deviations early and take corrective action.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Periodically assess the cost versus the expected benefits of the blockchain solution. If the costs outweigh the benefits, it may be necessary to reassess the project’s viability.
- Resource Allocation: Adjust resource allocation based on evolving project requirements. Shift resources to areas that have a higher impact on achieving objectives.
- Risk Assessment: Regularly assess project risks, including potential cost overruns, and develop contingency plans to mitigate these risks.
Benefits:
- Cost Control: Regular reviews and evaluations ensure that the project remains within budgetary constraints, minimizing the risk of financial surprises.
- Alignment with Objectives: By continuously assessing costs and benefits, you can ensure that the project’s objectives and expected returns remain in sync.
- Risk Mitigation: Proactive risk assessment and planning help mitigate cost-related risks and avoid budgetary crises.
Top Blockchain Application Services
Supply Chain Management: Companies like IBM and VeChain use blockchain to track and verify the authenticity of products throughout the supply chain, improving transparency and reducing fraud.
Healthcare Data Management: Healthereum and Medicalchain use blockchain to securely store and share patient health records while maintaining privacy and data integrity.
Gaming and Virtual Worlds:
Blockchain-based gaming platforms like Axie Infinity and Decentraland enable players to own and trade in-game assets as NFTs, creating new economies within virtual worlds.
Voting and Governance: Projects like Polkadot and Tezos explore blockchain solutions for secure and transparent voting systems and decentralized governance.
Legal and Notary Services: Blockchain-based platforms like Notary and Stampery provide secure and tamper-proof notarization and document verification services.
DApps and DLT: DApps (Decentralized Applications) and DLT (Distributed Ledger Technology) are at the heart of blockchain innovation. DApps are applications that run on decentralized networks, while DLT is the underlying technology that ensures transparency and security through a distributed ledger.
Smart Contracts Development: Smart Contracts Development involves creating self-executing contracts on blockchain platforms like Ethereum. These contracts automatically enforce and execute predefined rules and agreements without intermediaries. They ensure trust, security, and transparency in various applications, including finance, supply chain, and legal processes, revolutionizing how agreements are made and executed.
Crypto Wallets: Crypto Wallets serve as digital vaults for securely storing cryptocurrencies, ensuring easy access and safeguarding assets against potential threats.
Crypto Exchange: A crypto exchange is a digital marketplace where users can trade cryptocurrencies. It acts as a bridge between buyers and sellers, facilitating transactions and price discovery. These platforms offer various trading pairs and provide essential liquidity for the vibrant cryptocurrency ecosystem, making it accessible to users worldwide.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is a financial ecosystem built on blockchain technology, offering decentralized alternatives to traditional financial services. It includes lending, borrowing, trading, and earning interest on cryptocurrencies without intermediaries. DeFi platforms aim to increase financial accessibility, transparency, and user control, reshaping the future of finance.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) are unique digital assets representing ownership of one-of-a-kind items, art, collectibles, or virtual real estate on blockchain platforms. They cannot be exchanged on a one-to-one basis like cryptocurrencies because each NFT has distinct characteristics and provenance, making them valuable for digital ownership, proven authenticity, and digital art collectors.
ICO: ICO, short for Initial Coin Offering, is a fundraising method where new cryptocurrencies are sold to investors. White Papers outline the project’s concept, goals, and technical details, acting as a blueprint for ICOs.
- MVP, or Minimum Viable Product, is the first version of a product or service, showcasing its core functionality.
- Well-known Advisors bring expertise and credibility to blockchain projects, reassuring investors and users.
- Advertising and PR efforts are essential for creating awareness and trust in the project.
- Interaction on Social Channels is crucial for community engagement, fostering discussions, and sharing project updates and news.
These are examples of the many blockchain application services available. The blockchain ecosystem is constantly evolving, and new services and use cases continue to emerge as the technology matures and gains wider adoption.
Revolutionizing Industries with Blockchain Mobile App Development

In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, blockchain technology has emerged as a game-changer, promising transparency, security, and efficiency across various sectors. One of the most promising avenues for harnessing blockchain’s potential is through mobile app development. Let’s delve into the industries that stand to benefit immensely from this transformative technology:
Finance and Banking:
Blockchain mobile apps can revolutionize financial institutions by simplifying cross-border transactions, reducing fraud, and enhancing transparency. Users can securely manage their assets, access loans, and execute trades with minimal fees and maximum trust.
Supply Chain Management:
Supply chains are complex webs of transactions and information. Blockchain apps can streamline this process by providing real-time visibility, allowing stakeholders to track products from source to destination, reducing errors, and improving accountability.
Healthcare:
Blockchain mobile apps can secure medical records, ensuring that patients have control over their health data. This can enhance interoperability between healthcare providers, expedite insurance claims, and improve patient outcomes.
Real Estate:
Buying and selling property often involves intermediaries and lengthy paperwork. Blockchain apps can simplify real estate transactions by offering smart contracts, reducing fraud, and accelerating the process, making homeownership more accessible.
Supply Chain and Logistics:
Managing the movement of goods globally can be fraught with inefficiencies and vulnerabilities. Blockchain application development company can optimize supply chain processes, making it easier to trace the origin of products, verify authenticity, and enhance overall efficiency.
Education:
Blockchain can provide a secure platform for verifying educational credentials and achievements. Educational institutions can issue certificates and diplomas on the blockchain, making it easier for employers to verify qualifications.
Intellectual Property:
Protecting intellectual property rights is a priority for many industries. Blockchain mobile apps development company can ensure the authenticity and ownership of content, art, and inventions, reducing piracy and copyright infringement.
Voting and Elections:
Ensuring the integrity of elections is paramount. Blockchain apps can offer secure and transparent voting systems, enabling citizens to cast their votes remotely while safeguarding the accuracy and authenticity of the results.
Energy Sector:
Decentralized energy grids and trading platforms can be facilitated through blockchain app development company, allowing individuals and businesses to buy and sell excess energy securely and efficiently.
Retail and E-commerce:
Blockchain can be used to authenticate product origins, reduce counterfeit goods, and improve customer trust. Loyalty programs and payment systems can also benefit from blockchain-based apps.
Legal Industry:
Smart contracts and blockchain application development company can automate legal processes, making contracts more secure and self-executing. This can lead to reduced legal fees and quicker dispute resolution.
Government and Public Services:
Governments can use blockchain apps for identity verification, land registries, and the distribution of benefits and subsidies, ensuring transparency and reducing fraud.
Top-notch Tech Stack for Blockchain Application Development
Smart Contract Languages:
- Solidity: Ethereum’s primary language for writing smart contracts.
- Rust: Used for developing smart contracts on Polkadot’s Substrate framework.
- Vyper: A Python-based alternative to Solidity for Ethereum.
Blockchain platforms:
Blockchain platforms are the foundational layer of a top-notch tech stack for blockchain application development company. These platforms, such as Ethereum development, Binance Smart Chain, and Polkadot, provide the infrastructure for building decentralized applications (DApps) and executing smart contracts. They offer essential features like consensus mechanisms, security, and scalability, serving as the backbone for developers to create innovative blockchain development solutions. Choosing the right platform is crucial as it impacts the performance, capabilities, and interoperability of the final application.
Development Frameworks:
- Truffle: A development framework for Ethereum DApps with tools for smart contract testing, deployment, and management.
- Hardhat: Offers a development environment for Ethereum that is highly extensible and suitable for professional developers.
- Substrate: For building custom blockchains and parachains on Polkadot.
Wallet Integration:
Crypto Wallet integration is a critical aspect of a top-notch tech stack for blockchain application development. Cryptocurrency Wallets like MetaMask and MathWallet enable users to interact with decentralized applications (DApps) securely. They provide key functionalities, such as private key management, transaction signing, and asset storage. Integrating these wallets into DApps simplifies the user experience, fostering wider adoption and usability, while ensuring the security and control of users’ digital assets.
Oracles:
- Chainlink: For fetching real-world data and integrating it into smart contracts securely.
- Band Protocol: Another option for decentralized oracles.
Identity Management:
Identity management is an integral part of a top-notch tech stack for blockchain application development. Utilizing decentralized identity standards like DID (Decentralized Identifiers) and Verifiable Credentials ensures secure, user-controlled authentication and identity verification. This enhances privacy and security in blockchain applications, enabling users to maintain control over their personal data and interact with DApps and services seamlessly while mitigating identity fraud and enhancing trust in the blockchain ecosystem.
Monitoring and Analytics:
- Prometheus and Grafana: For monitoring blockchain nodes and applications.
- Etherscan/BscScan: Block explorers for Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain.
Consensus Mechanisms:
Consensus mechanisms are a vital element of a top-notch tech stack for blockchain application development. They dictate how transactions are validated and added to the blockchain. Options like Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and Proof of Work (PoW) impact scalability, security, and energy efficiency. Choosing the right consensus mechanism is essential, as it directly influences the blockchain’s performance and reliability, aligning it with the application’s goals and requirements.
Interoperability:
- Polkadot Bridge: For connecting with other blockchains.
- Cosmos IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication): For interoperability in the Cosmos ecosystem.
Testing and Deployment:
Testing and deployment tools are essential components of a top-notch tech stack for blockchain application development. Tools like Ganache and Docker simplify the testing and deployment processes, allowing developers to ensure their smart contracts and DApps function as intended. Kubernetes further aids in managing containerized applications in production environments, ensuring scalability and reliability. These tools streamline development workflows and enhance the efficiency and stability of blockchain applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing blockchain development costs while delivering essential features is a multifaceted endeavor crucial for the success of blockchain projects. By meticulously defining objectives and requirements, prioritizing features, optimizing resources, and continually reviewing costs, organizations can strike a balance between innovation and fiscal responsibility. This approach not only ensures the development of efficient and effective blockchain solutions but also enhances adaptability and alignment with business goals. Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of costs and features empowers organizations to harness the transformative potential of blockchain technology while maintaining financial discipline and achieving meaningful outcomes in various industries.
How do different blockchain platforms impact development costs and features?
Different blockchain platforms have varying impacts on development costs and features. Ethereum, for instance, is widely adopted and offers robust smart contract capabilities but can be costly due to high gas fees. In contrast, the Binance Smart Chain provides lower-cost transactions, but with some trade-offs in decentralization. Meanwhile, platforms like Polkadot emphasize interoperability and scalability.
Features also differ based on the platform. Ethereum's rich ecosystem includes DeFi applications, while Binance Smart Chain focuses on fast transactions for similar use cases. Polkadot's parachains enable customized blockchains within the network, offering unique features.
Can you explain the typical stages of blockchain development and their associated costs?
Blockchain development typically involves stages like concept validation, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. Costs vary widely depending on the complexity of the project, platform, and team. Concept validation and design are relatively low-cost stages, while development and testing can be resource-intensive. Deployment and ongoing maintenance costs include hosting, security, and updates.
Are there any cost-saving strategies or best practices for managing blockchain development expenses?
Cost-saving strategies include using open-source tools, reusing code, optimizing smart contracts for gas efficiency, and exploring blockchain-as-a-service platforms. Collaboration within the blockchain community can also reduce costs through shared resources and knowledge.
How does scalability influence both the cost and functionality of a blockchain solution?
Scalability impacts costs by affecting transaction fees and infrastructure requirements. Functionality improves with scalability, allowing more transactions per second and broader adoption.
Can you provide insights into the cost comparison between building a blockchain from scratch and using existing platforms?
Building a blockchain from scratch is significantly more expensive and time-consuming than using existing platforms. Custom blockchains require extensive development, security audits, and ongoing maintenance, whereas existing platforms offer proven infrastructure at a fraction of the cost and time. However, building from scratch may be necessary for unique use cases or advanced features

Mr. Saddam Husen, (CTO)
Mr. Saddam Husen, CTO at Comfygen, is a renowned Blockchain expert and IT consultant with extensive experience in blockchain development, crypto wallets, DeFi, ICOs, and smart contracts. Passionate about digital transformation, he helps businesses harness blockchain technology’s potential, driving innovation and enhancing IT infrastructure for global success.
Based on Interest

Cryptocurrency Exchange Development: How to Create a Platform Like Binance or Coinbase
The rise of cryptocurrency has revolutionized the financial world, creating new avenues for investment, trading, and technology-driven finance. Among the major…

Layer 1 vs Layer 2 Blockchain: Key Differences, Use Cases & Which One Matters More in 2025
Introduction Blockchain technology, once the exclusive domain of cryptocurrencies, has now evolved into a robust tool for various industries, including finance, healthcare,…